[SpringBoot] Swagger2로 Rest API 문서화 및 테스트 하기
오늘은 Swagger2라는 API 문서 자동화 도구를 소개하려고 한다.
우리가 Spring Boot를 통해 Rest API를 개발하게 되면 요즘 같은 백엔드와 프런트엔드의 업무 구분이 나누어져 있는 경우
API 문서를 상대방에게 제공해 주어 협업을 진행해야 한다. 그러나 개발을 하고 또다시 문서화를 하는 건
여간 번거로운 일이 아니다. 일단 그리고 개발자라서 그런가 문서작업이 쉽지 않은 것도 있다.
그럴 때 이제 사용할 수 있는 게 Swagger2라는 문서화 도구인데 비교 대상으로는 Spring Rest Doc이라는 게 있다.
각각의 장단점이 있겠지만 Swagger2를 소개하니 Swagger2의 장점을 몇 개 말해보면
일단 환경설정이 무엇보다 간편하고 테스트를 할 수 있어 데이터를 확인해볼 수 있다.
단점으로는 아무래도 기존 개발코드와 직접적인 관련이 없는 어노테이션과 코드가 들어가 코드가 지저분해질 수도 있다는 건데
장점으로 얻는 게 아무래도 더 크기 때문에 백엔드 개발자라면 배워두면 유용하게 사용 가능하다.
1. build.gradle 추가
build.gradle에 아래와 같이 설정해 준다.
여기서 하나 알아두어야 할게
2.9.2버전으로만 사용하게 되면 Swagger가 시작될 때 이유를 할 수 없는 에러가 발생한다.
인터넷에 찾아보니 해당 내부 라이브러리 이슈로 판단되어 아래와 같이 바꿔주면 해당 에러는 사라지는 걸 확인했다.
ext {
swagger2Version = '2.9.2'
oldSwagger2Version = '1.5.21'
}
dependencies {
.....
/*--------------------------[ Swagger 2 ]--------------------------------*/
// Swagger2 내부 라이브러리 이슈로 인한 Annotatios과 Models 과거 버전으로 사용
//implementation 'io.springfox:springfox-swagger2:2.9.2'
implementation 'io.springfox:springfox-swagger-ui:2.9.2'
implementation("io.springfox:springfox-swagger2:${swagger2Version}") {
exclude group: 'io.swagger', module: 'swagger-annotations'
exclude group: 'io.swagger', module: 'swagger-models'
}
implementation "io.swagger:swagger-annotations:${oldSwagger2Version}"
implementation "io.swagger:swagger-models:${oldSwagger2Version}"
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
}
2. Java Configration 추가
useDefaultResponseMessages(false)를 해주면
기본으로 가지고 있는 400,404,500 에러 등을 표시 안 해준다.
오늘은 여러 가지 설정법을 알아볼 예정이니 false로 설정해 주고
추후 필요한 부분이 있으면 본인에 맞게 설정 바란다.
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfiguartion {
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
//.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any()) // 모든 RequestMapping URI 추출
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/v2/**")) // 경로 패턴 URI만 추출
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.demo")) // 패키지 기준 추출
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.useDefaultResponseMessages(false); // Response 응답 메시지 디폴트값 적용 X
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("REST API")
.description("스프링부트 샘플 프로젝트")
.version("v1")
.termsOfServiceUrl("서비스 약관 URL")
.contact("본인 이메일")
.license("License")
.licenseUrl("localhost:8080")
.build();
}
}
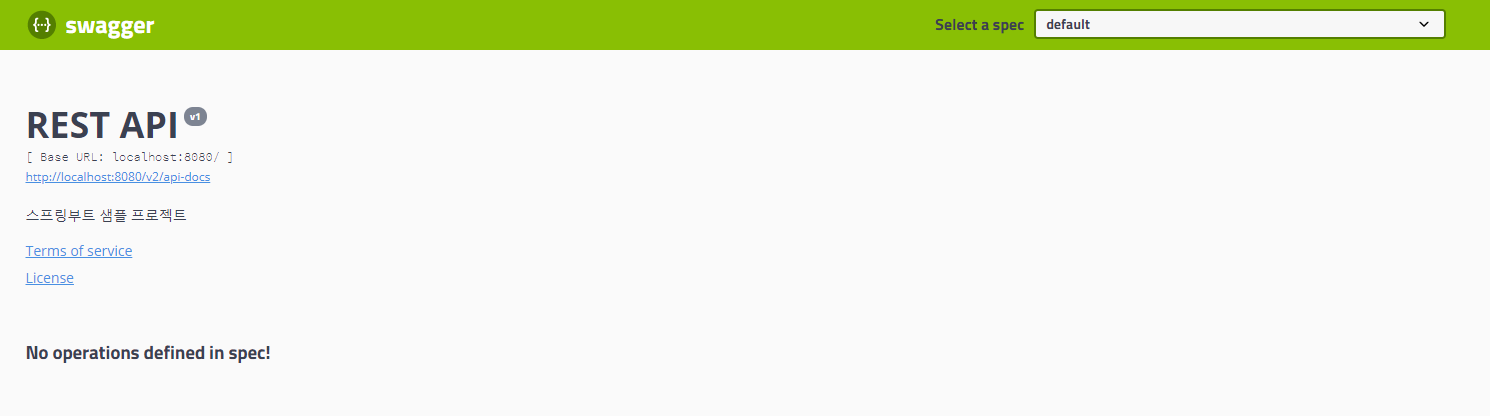
이제 Spring Boot를 실행시켜
URL에 **http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html#/**를 입력해보면
아래와 같은 화면이 뜨면 정상적으로 Swagger2 기초 설정이 완료되었다.
- 여기서 하나 팁으로는 description에 대한 값은 String으로 하여 HTML문법을 사용해주면
좀 더 다양한하게 설명이 가능하다.
3. Controller에 Swagger 어노테이션 추가
@RestController
@Api(tags = { "1. Swagger Test" }) // Swagger 최상단 Controller 명칭
//@ApiIgnore // 제외처리
public class SwaggerController {
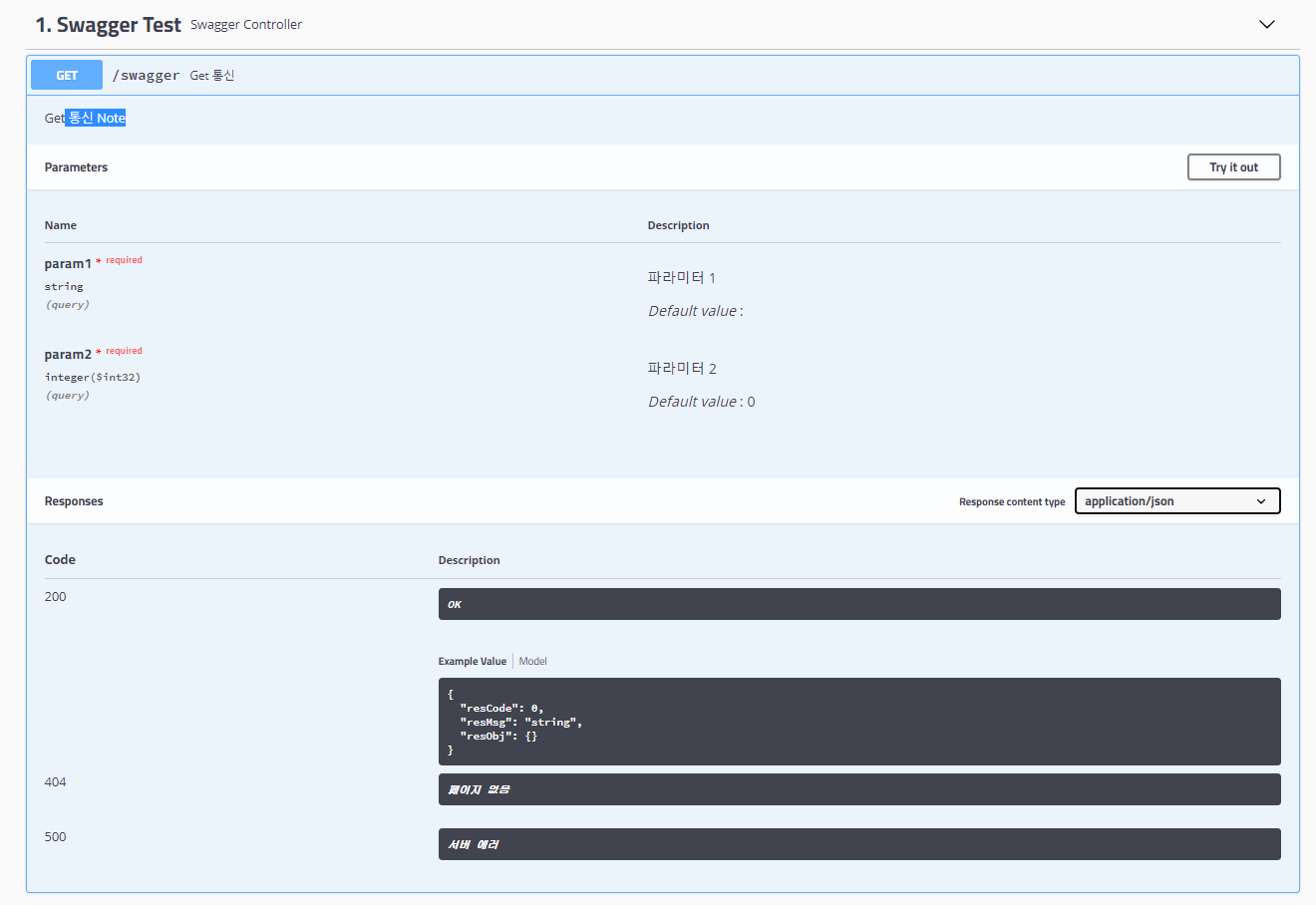
@ApiOperation(value = "Get 통신", notes = "Get 통신 Note", response = String.class) // value: 해당 파라미터 명칭, notes : 메소드에 대한 설명란
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(code = 404, message = "페이지 없음"),
@ApiResponse(code = 500, message = "서버 에러")
})
@GetMapping(value = "/swagger", produces = "application/json")
public String GetRestApi(
@ApiParam(value = "파라미터 1", required = true) @RequestParam(required = true, defaultValue = " ") String param1,
@ApiParam(value = "파라미터 2", required = true) @RequestParam(required = true, defaultValue = "0") int param2 ) {
String result = "테스트";
return result;
}
}
- @Api : tag 옵션 값으로 Controller 명칭을 지정해 줄 수 있다.
- @ApiIgnore : 해당 Controller를 Swagger 페이지에서 보이지 않게 해준다.
- @ApiOperation : 해당 메소드의 설명을 나타내 준다.
- value : 간단하게 메소드의 설명을 적어준다.
- note : 좀 더 자세하게 메소드의 설명을 적어준다.
- response : Response 타입을 지정해 준다. (지정하여 주지 않으면 Response객체를 파악하여 형태를 보여준다.)
- @ApiResponses : Response 에러 설명을 나타내 준다.
- @ApiResponse : Response Code와 Message를 적어준다.
- @ApiParam : 해당 파라미터에 대한 설명을 나타내 준다.
- value : 파라미터의 대한 설명을 적어준다.
- required : 필수 값을 설정
위와 같이 설정했을 때 어떠한 화면이 보이는 알아보자.
이외에도 더 다양한 설정값과 옵션이 있으니 그건 아래의 링크를 확인해보길 바란다.
https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-core/wiki/Swagger-2.X---Annotations#quick-annotation-overview
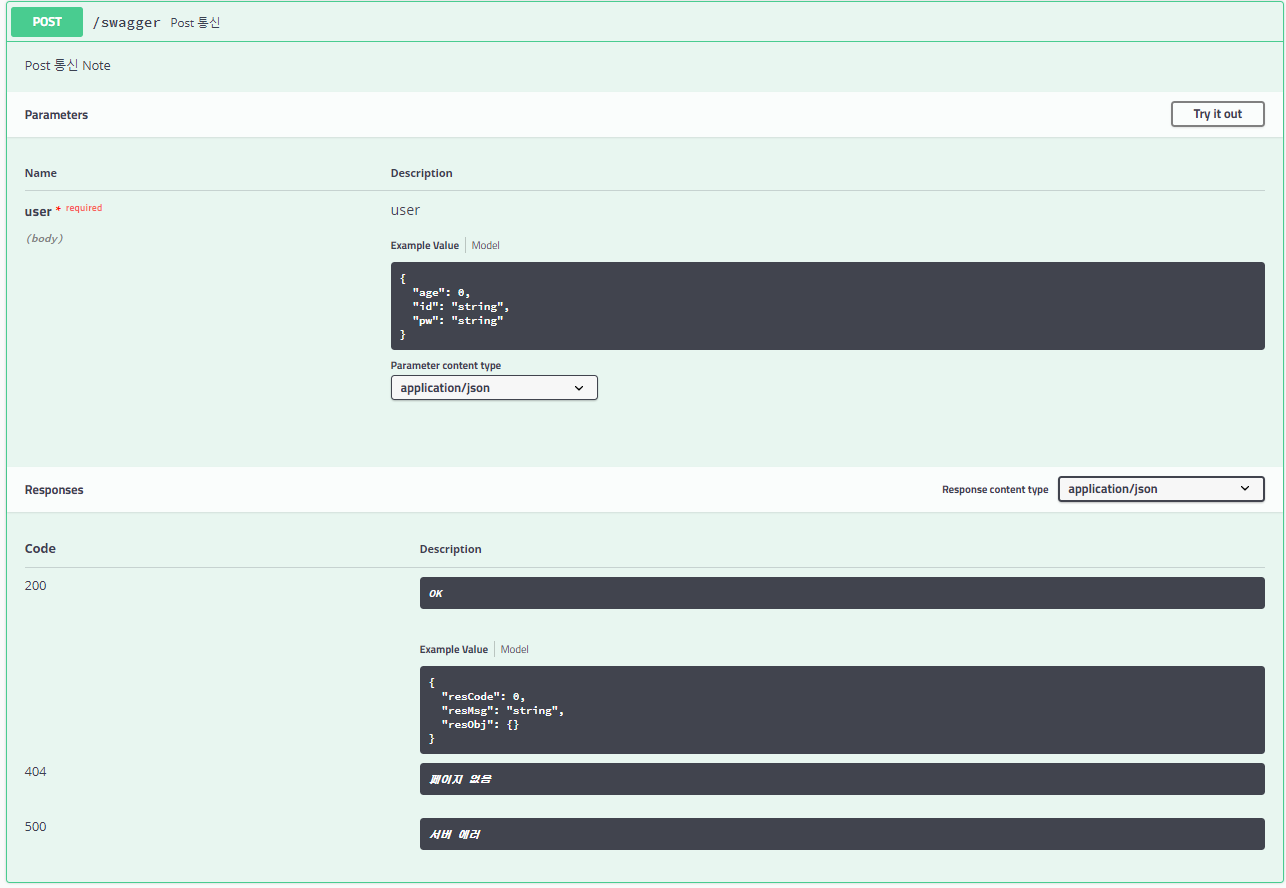
또한 Post 통신할 때 객체 그 자체로 데이터를 받는 RequestBody 형식에는 파라미터를 어떻게 표현하는지 알아보자
@ApiModel
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "아이디", required = true)
private String id;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "패스워드", required = true)
private String pw;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "나이", required = true)
private int age;
}
- @ApiModel : 해당 클래스가 Api 통신할 때 사용되는 클래스임을 명시해 준다.
- @ApiModelProperty : 해당 변수의 설명을 나태내 준다.
- value : 변수에 대한 간단한 설명을 적어준다.
- note : 변수에 대한 자세한 설명을 적어준다.
- required : 필수 값을 설정
- hidden : Hidden
@ApiOperation(value = "Post 통신", notes = "Post 통신 Note", response = String.class)
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(code = 404, message = "페이지 없음"),
@ApiResponse(code = 500, message = "서버 에러")
})
@PostMapping(value = "/swagger", produces = "application/json")
public String PostRestApi(@RequestBody User user) {
String result = "테스트";
return result;
}
해당 화면에서 Try it out 버튼을 통해 파라미터를 던져 데이터를 확인해볼 수 있다.
오늘은 간단하게 Swagger2 설정법과 사용법을 알아 보았다.
그래도 개발자라면 Word나 Excel보단 IDE에서 작업하여 문서화하는 게 실수도 적고 직관적이고 좋을 거다.
공식 홈페이지를 보니 꼭 Spring에 국한되어 있지 않고 다양한 프레임워크에서 지원하니 다른 언어에서도 사용해보면 좋을 거 같다.